Some Important Facts About Ovarian Cysts
In these article we will Illustrate some Facts About Ovarian Cysts, I believe these will go a long way to answer some questions.
INTRODUCTION
Human reproduction is a complex process which involves the production of healthy gene cells, spermatozoa in relation to the male and oocytes in relation to the female.
There is also a need for patient fallopian tubes that will not allow the germ cell to arrive at the site if fertilization.
The capacity of the spermatozoa to fertilize the ovum, the ability of the zygote to migrate and implant in the endometrial lining of the uterus, a healthy viable environment for embryonic growth and fetal development.
Though all these are important in the complex process of human reproduction, the most important factors in the course are viable precursors, testes and ovaries.
The ovaries are primarily reproductive organs for the female reproductive system. They perform the dual function of producing germ cells(Ova, which are released during Ovulation) and secreting the female sex hormones, Oestrogen and progesterone. These functions are essential for ovulation and fertility. A disruption in these may emerge in the form of CYSTS.
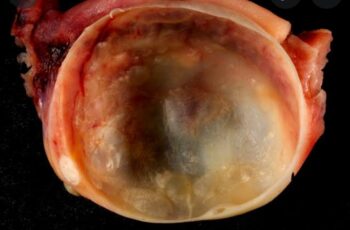
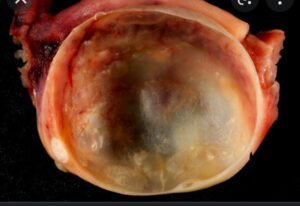
An Ovarian cyst is an empty or fluid-filled sac found within or on the surface of the ovary. It varies in size from less than one centimeter to greater than ten centimeter.
Ovarian cyst could be functional or pathological. These develop from the normal function of the menstrual cycle and abnormal cell growth respectively.
Against this backup, therefore, this work seeks to explore the concept of ovarian cyst as they pertain to the female reproductive system. It takes cognizance of their various types, diagnosis, clinical features, pathogenesis, epidemiology, risk factors, complications, prognosis, differential diagnosis, management, follow up and treatment.
DEFINITION
It is a small cyst to develop on the ovaries because the ovaries is complex in it’s embryology, histology, steroidogenesis and has the potential to develop malignancy.
A cyst is abnormal but usually a noncancerous growth filled with liquid or a semisolid substance sometimes causing pain.
Ovarian cyst which is known to be small sacs filled with fluid that are situated in the ovaries or on its surface and exhibit wide variation in structure and biological behavior occuring in any age occurs if the follicle ( that which releases the egg into a fallopian tube about once a month) doesn’t release the eggs.
The unreleased egg grows bigger and develop into a FOLLICLE CYST or CORPUS LIUTHEUM CYST. Its also possible for the unreleased egg to develop something called DERMOID CYSY which forms when cells in the ovary starts dividing even though they haven’t been fertilized.
This type of cyst contains the genetic materials for a human life (hair, teeth, nails).Most premenopausal women and 15% of post menopausal women are found to have Ovarian cyst as any ovarian follicle which is larger than approximately 2cm is an ovarian cyst.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The incidence of ovarian cyst in the general population is difficult to estimate. The epidemiology of ovarian cyst is unclear due to the lack of consistent reporting and a high likelihood of spontaneous resolution.
– Estimates of the prevalence of ovarian cyst vary widely with most authors reporting between 8% and 18% of both premenopausal and postmenopausal women having ovarian cyst. most premenopausal cyst persist for years.
– In the united States, approximately 5% to 10% of women undergo surgical exploration for ovarian cyst in their lifetime though only 13% to 21% of these cyst are malignant.
– Pre-surgical evaluation of ovarian cyst is critical to prevent unnecessary surgical intervention while still detecting potential malignancy.
– For the vast majority of women, ovarian cyst are not precancerous lesions and do not increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer later in life. Removal of benign cysts does not decrease future mortality from ovarian cancer.
RISK FACTORS
A risk factor which is known as something/characteristics/conditions that increases the chance of a person developing a disease or condition isn’t exempted in the case of ovarian cyst. The risk factors of ovarian cyst includes ; Obesity, late menopause, Early menstruation, Ovulation Induction, Infertility, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, Hyperthryoidism, Age(20-80) and Hormone Replacement therapy containing Oestrogen Only.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
During normal ovulation, a follicle matures and then ruptures releasing an oocyte (egg).If the follicle fails to rupture and instead continued to grow, a follicular cyst develops. After Ovulation, the corpus luteum forms and subsequently involutes. When the Corpus luteum fails to involute and continues to grow, a corpus luteum cyst occurs.
Both types of Cyst are considered physiologic or functional and neither have any malignant potential. These types of Cyst are benign and may resolve voluntarily but over a pathological course, they maybe infected there by leading to several complications.
CLINICAL FEATURES
The clinical features of Ovarian Cyst includes; Chronic Pelvic Pain which may develop secondary pressure on the bladder or bowel also causing frequency or constipation. It may also manifest as dyspareunia or cyclical pain in those patients with endometriosis who have developed chocolate cysts. – Acute Pain which could be as a result of bleeding into cyst, rupture or torsion. – Discomfort with intercourse particularly deep penetration. – Bleeding Per Vagina , – Abnormal genital Tract bleeding, – Nausea and Vomiting, – Adnexal mass.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Hermorrhagic Corpus Luteum Cysts, Dermoid (Mature Cystic Teratomas), Endometriomas, Pedunculated Fibroids, Hydrosalpinges, Paratubal and paraovarian cysts, Peritoneal Inclusion Cysts, Pelvic Kidneys, Appendiceal or Diverticular Abscess, Ectopic pregnancy.
DIAGNOSIS: Pelvic Scan, Blood tests, Ultrasound, Laparoscopy.
COMPLICATIONS
Ovarian Cyst could be complicated thereby leading to; Torsion, Rupture, Infection, Pseudomyxoma Peritoni, Extraperitoneal Spread, Secondary malignant Change, Intracystic hemorrhage, Abdominal Adhesion.
PROGNOSIS: Early Detection is the key to the success of management because with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment the prognosis of ovarian cyst is excellent.
– Ovarian Cyst Salvage rate is below 10% in adult due to delay in diagnosis.
-Uncomplicated cysts are usually managed conservatively with success rates less than 95% and these patients can lead normal lives.
-Patients who undergo surgeries in uncomplicated situations have their fertility preserved because pregnancy outcome associated with Adnexal torsion generally is good.
-Late presentation accounts for about 49% of all ovarian surgical emergencies.
TREATMENT; Treatment of ovarian cyst depends on the size of the Cyst, the type of cyst, the patients future pregnancy plans, the symptoms the patients is experiencing and general health. Otherwise, ovarian cyst can be treated through watchful waiting (regular monitoring) in the case of a small asymptomatic cysts, medications and surgery (which is more likely to be a cyst more than 5-10cm).
CONCLUSION; Most premenopausal women and 15% of postmenopausal women are found to have Ovarian Cyst.
-Any ovarian follicle that is larger than approximately 2cm is an ovarian cyst.
-Large cyst (more than 5-10cm) are more likely to require surgical removal.
– A large size doesn’t not predict whether a cyst is cancerous.
– Whether the surgery involves removing only the cyst or the entire ovary depends on one’s age and what’s found during examination.
– Having one ovary removed will not cause menopause and infertility because no matter how much it gets abused the body can restore balance.
-There is no definite way of preventing ovarian Cyst growth. Healthy lifestyle may prevent it, regular check-ups can help treat complications because I believe that the greatest gift you can give your family is healthy you.